Best of Both Worlds? Combining Remoted Piloted Aircraft (RPA) LiDAR and Traditional Topographic Survey Methods.
The Background
- Date
- November 2023
- Client
- Innova
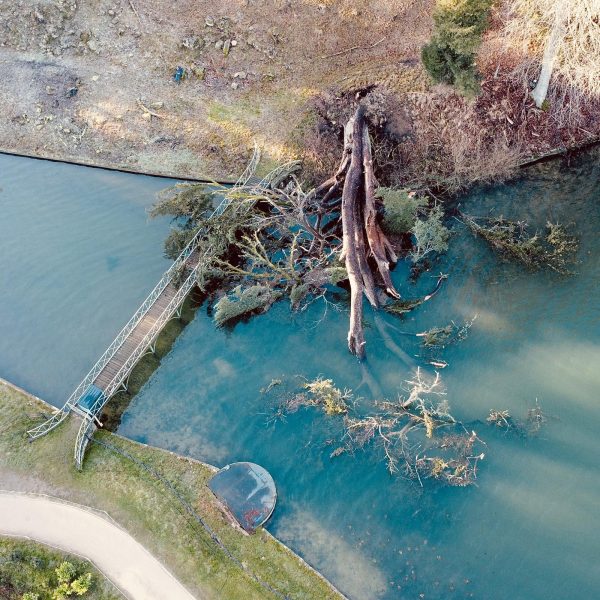
The Gleaston Survey aimed to combine LiDAR technology alongside traditional survey methods to map hidden channels in vegetated areas and along ditches. Commissioned by Innova, a green energy company, the project sought precise topographic data to aid in their environmental assessment and development of sustainable energy solutions.
The primary objective was to conduct a comprehensive topographic survey of the Gleaston area, targeting vegetated channels and ditches. This involved employing RPA LiDAR technology to cover the vast open areas efficiently and using traditional topographic survey methods in vegetated areas for better precision. The final goal was to amalgamate data from these varied sources to generate a combined topographic result.
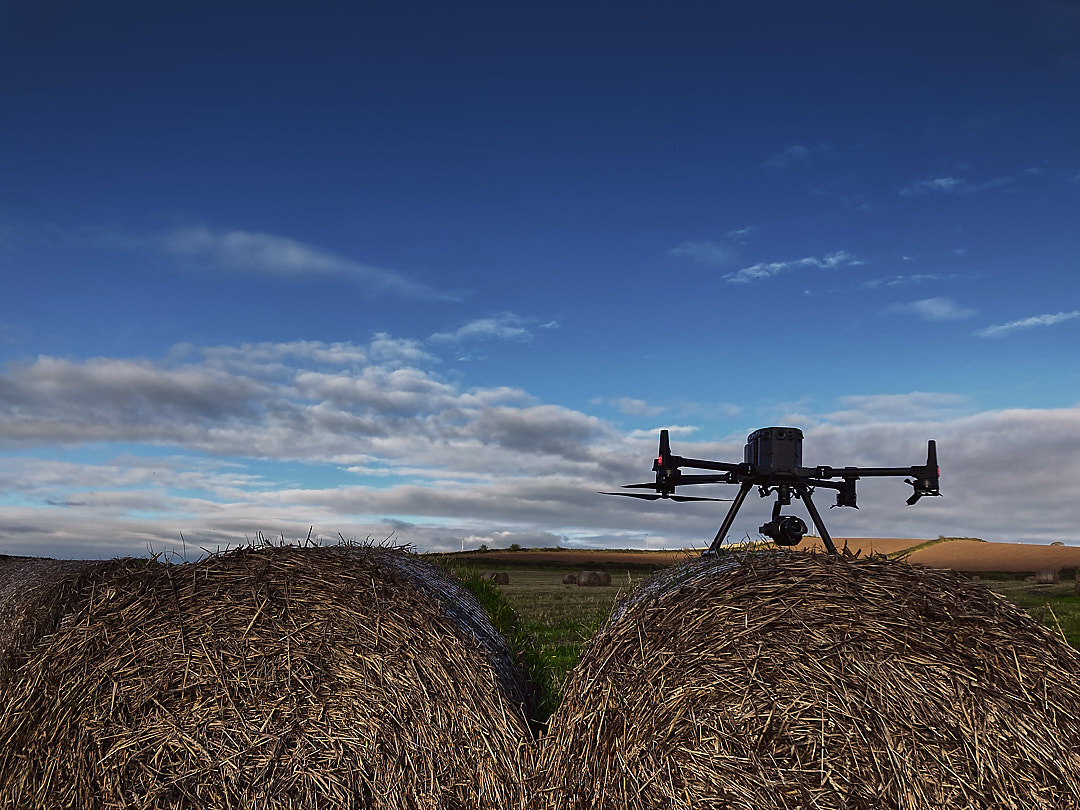
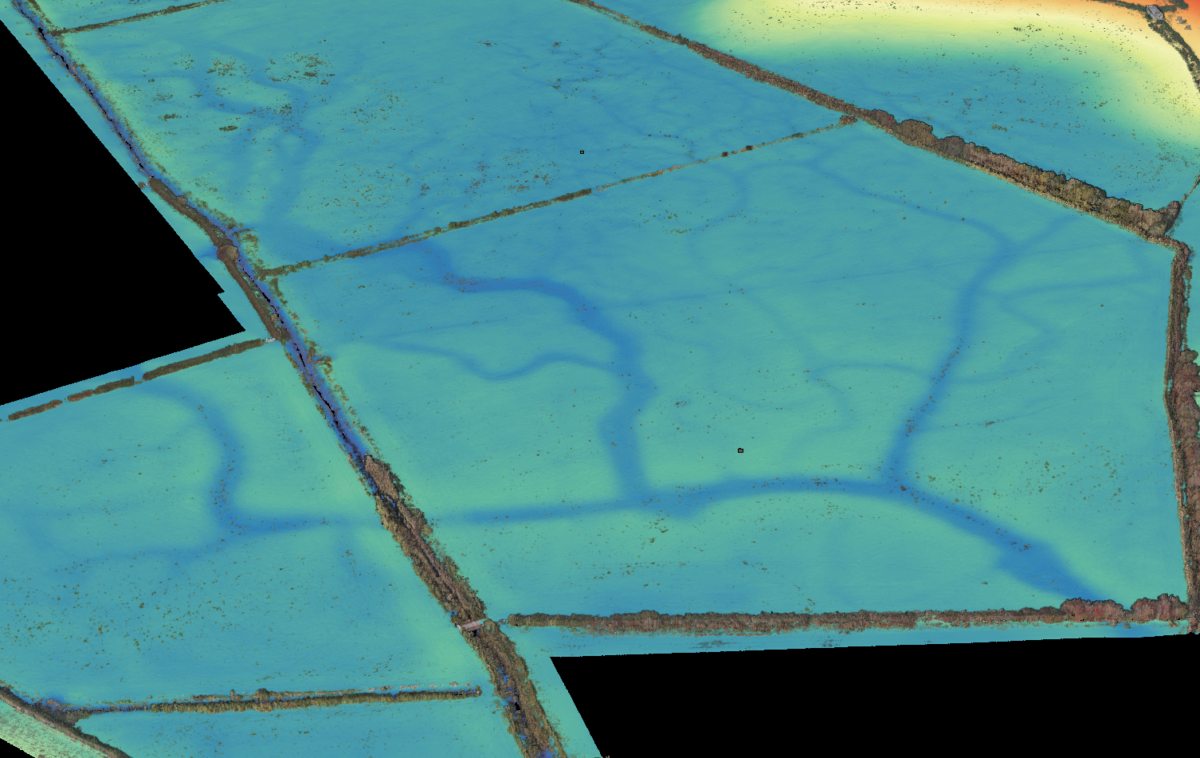
RPA LiDAR Mapping: Storm Geomatics’ M350 RPA equipped with the L1 was deployed to cover large expanses of the survey area. LiDAR sensors emitted laser pulses, allowing for the measurement of precise distances to the ground, penetrating through some vegetation and capturing elevation data in challenging terrains.
Traditional Topographic Survey: In areas with high vegetation density and along ditches where UAV LiDAR faced limitations, traditional topograhic survey methods were employed. Surveyors utilised total stations and GNSS receivers to collect accurate elevation and topographic data manually.
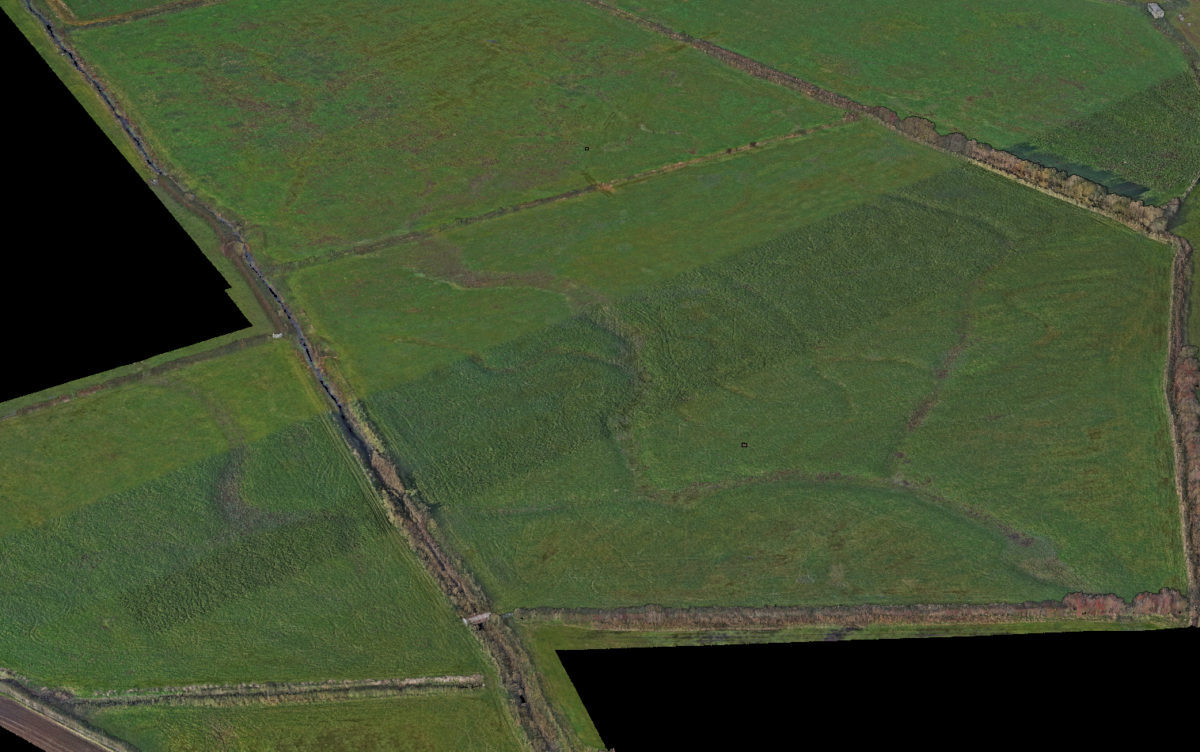
DJI P1 Camera for Orthomosaic: To complement the LiDAR data, a DJI P1 camera was utilised to capture high-resolution aerial images. These images were processed to create a 2D orthomosaic, providing additional visual context to the topographic survey.
Challenges
Complex Terrain: The presence of high and medium vegetation and ditch networks required a combination of surveying methods, adding complexity to data acquisition and processing. Moreover, this needed to be supplemented with conventional techniques because a portion of the survey area was underwater because of excessive rain.
Results
Integrating data from RPA LiDAR, traditional topographic surveys, and the orthomosaic generated from the P1 camera facilitated the creation of a comprehensive set of deliverables with high accuracy and detailed information about hidden channels, substantial trees, fence lines and buildings.
The Gleaston Topographic Survey perfectly demonstrated the synergy between RPA LiDAR technology and traditional survey methods in challenging environments. Despite weather challenges, the combination of these techniques provided Innova with an accurate topographic dataset imperative for their green energy initiatives and environmental impact assessment.
This case study highlights the effectiveness of utilising multiple surveying methodologies to overcome obstacles and deliver comprehensive topographic results beneficial for sustainable development projects.
Recent News
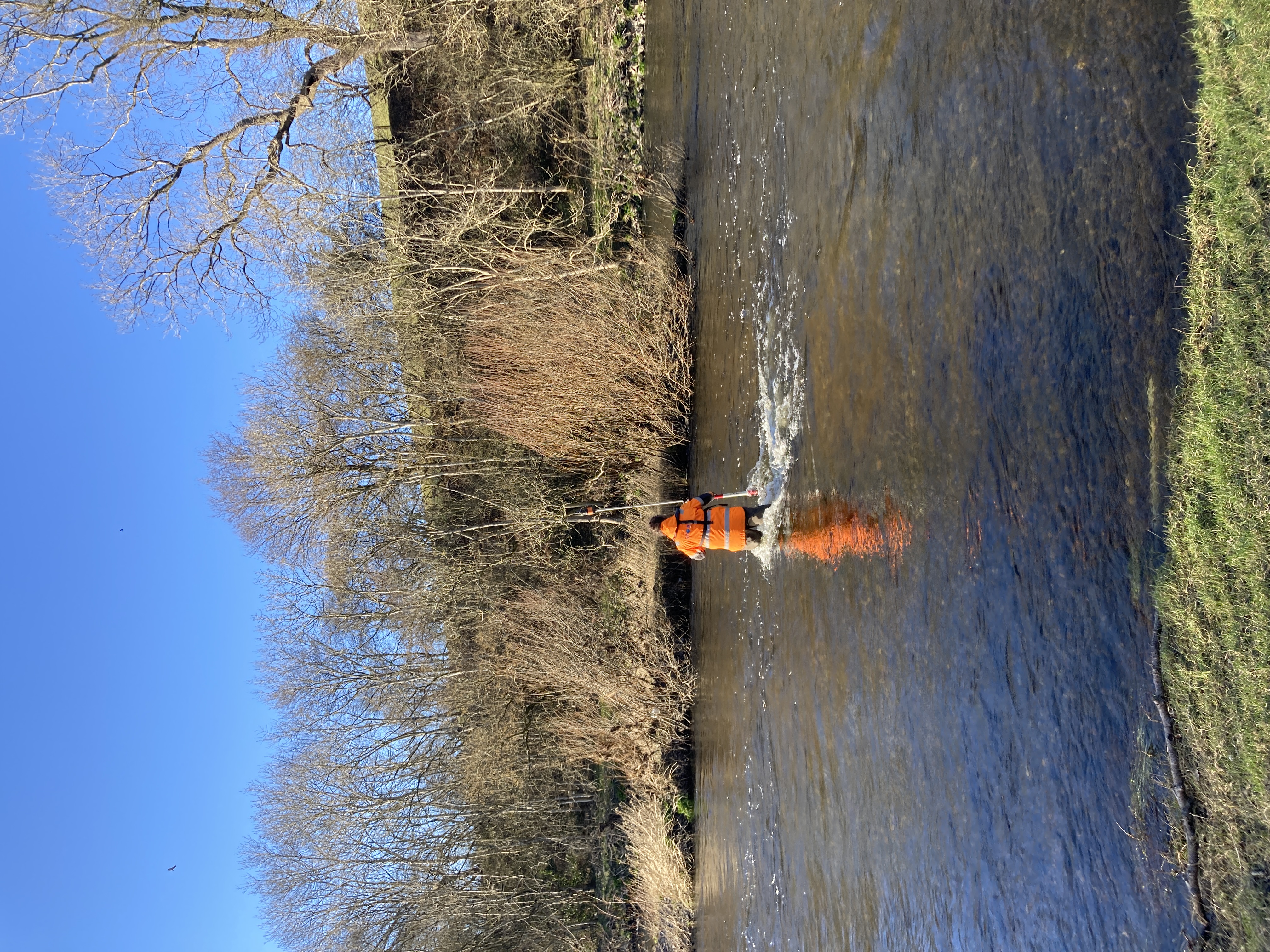

From Dee to Data: Storm Delivers Dynamic River Data

What’s Driving Our Success in Surveys & Leadership?